SQL刷题笔记
SQL刷题笔记
基础题:
表 user_profile
| id | device_id | gender | age | university | province |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2138 | male | 21 | 北京大学 | Beijing |
| 2 | 3214 | male | 复旦大学 | Shanghai | |
| 3 | 6543 | female | 20 | 北京大学 | Beijing |
| 4 | 2315 | female | 23 | 浙江大学 | ZheJiang |
| 5 | 5432 | male | 25 | 山东大学 | Shandong |
1.查看用户信息表中所有的数据,请你取出相应结果 select * from user_profile
2.想要用户的设备id对应的性别、年龄和学校的数据,请你取出相应数据
select device_id,gender,age,university from user_profile;
3.查看用户来自于哪些学校,请从用户信息表中取出学校的去重数据
(1)select DISTINCT university from user_profile;
(2)select university from user_profile group by university;
4.查看前2个用户明细设备ID数据,请你从用户信息表 user_profile 中取出相应结果
select device_id from user_profile limit 0,2;
5.查看前2个用户明细设备ID数据,并将列名改为 user_infos_example,从用户信息表取出相应结果
select device_id user_infos_example from user_profile limit 0, 2;
(原列名) 省略as (新列名)
6.想要筛选出所有北京大学的学生进行用户调研,请你从用户信息表中取出满足条件的数据,结果返回设备id和学校
select device_id,university from user_profile where university=’北京大学’;
7.想要针对24岁以上的用户开展分析,请你取出满足条件的设备ID、性别、年龄、学校
select device_id,gender,age,university from user_profile where age>24;
8.想要针对20岁及以上且23岁及以下的用户开展分析,请你取出满足条件的设备ID、性别、年龄。
select device_id,gender,age from user_profile where age>19 and age<24;
9.想要查看除复旦大学以外的所有用户明细,请你取出相应数据
(1)select device_id,gender ,age, university from user_profile where university !=’复旦大学’;
(2)select device_id,gender ,age, university from user_profile where university NOT IN("复旦大学");
10.剔除没有获取到年龄的用户,请你取出所有年龄值不为空的用户的设备ID,性别,年龄,学校的信息
select device_id,gender ,age, university from user_profile where age !=”NULL”;
user_profile
| id | device_id | gender | age | university | gpa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2138 | male | 21 | 北京大学 | 3.4 |
| 2 | 3214 | male | 复旦大学 | 4.0 | |
| 3 | 6543 | female | 20 | 北京大学 | 3.2 |
| 4 | 2315 | female | 23 | 浙江大学 | 3.6 |
| 5 | 5432 | male | 25 | 山东大学 | 3.8 |
11.想要找到学校为北大或GPA在3.7以上(不包括3.7)的用户进行调研,请你取出相关数据(使用OR实现)
select device_id,gender,age,university,gpa from user_profile where university =”北京大学” or gpa >3.7;
12.想要找到学校为北大、复旦和山大的同学进行调研,请你取出相关数据
select device_id,gender,age,university,gpa from user_profile where university IN (‘北京大学’,’复旦大学’,’山东大学’);
13.找到gpa在3.5以上(不包括3.5)的山东大学用户 或 gpa在3.8以上(不包括3.8)的复旦大学同学进行用户调研,请你取出相应数据
select device_id,gender,age,university,gpa from user_profile where (university =”山东大学” and gpa >3.5) or (university=”复旦大学” and gpa>3.8);
14.查看所有大学中带有北京的用户的信息,请你取出相应数据。
select device_id,age,university from user_profile where university like ‘%北京%’;
15.想要知道复旦大学学生gpa最高值是多少,请你取出相应数据
(1)SELECT gpa FROM user_profile WHERE university=’复旦大学’ HAVING max(gpa);
(2)SELECT MAX(gpa) FROM user_profile WHERE university=’复旦大学’;
16.想要看一下男性用户有多少人以及他们的平均gpa是多少,用以辅助设计相关活动,请你取出相应数据
select count(gender) as male_num ,avg(gpa)from user_profile where gender=’male’;
17.现在运营想要对每个学校不同性别的用户活跃情况和发帖数量进行分析,请分别计算出每个学校每种性别的用户数、30天内平均活跃天数和平均发帖数量。
SELECT gender,university,COUNT(gender),avg(active_days_within_30)as avg_active_days,
avg(question_cnt)as question_cnt from user_profile
GROUP by gender,university
18.想查看每个学校用户的平均发贴和回帖情况,寻找低活跃度学校进行重点运营,请取出平均发贴数低于5的学校或平均回帖数小于20的学校
select university,avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt,avg(answer_cnt) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile 可以省略as
group by university
having avg_question_cnt<5 or avg_answer_cnt <20;
19.想要查看不同大学的用户平均发帖情况,并期望结果按照平均发帖情况进行升序排列,请你取出相应数据。
SELECT university,AVG(question_cnt)avg_quesition_cnt
FROM user_profile
GROUP BY university
ORDER BY avg_quesition_cnt ASC;//降序 DESC
20.查看所有来自浙江大学的用户题目回答明细情况,请你取出相应数据
select device_id,question_id,result
from question_practice_detail
where device_id = (select device_id
from user_profile
where university = ‘浙江大学’)
question_practice_detail
| id | device_id | question_id | result | date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2138 | 111 | wrong | 2021-05-03 |
| 2 | 3214 | 112 | wrong | 2021-05-09 |
| 3 | 3214 | 113 | wrong | 2021-06-15 |
| 4 | 6543 | 111 | right | 2021-08-13 |
| 5 | 2315 | 115 | right | 2021-08-13 |
| 6 | 2315 | 116 | right | 2021-08-14 |
| 7 | 2315 | 117 | wrong | 2021-08-15 |
21.想要了解2021年8月份所有练习过题目的总用户数和练习过题目的总次数,请取出相应结果
select
count(distinct device_id) as did_cnt,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where date like “2021-08%”
22.将用户划分为25岁以下和25岁及以上两个年龄段,分别查看这两个年龄段用户数量
SELECT if(age<25 OR age IS null,”25岁以下”,”25岁及以上”) as age_cut,
count(user_profile.device_id) as number
FROM user_profile
GROUP BY age_cut
23.将用户划分为20岁以下,20-24岁,25岁及以上三个年龄段,分别查看不同年龄段用户的明细情况,请取出相应数据。(注:若年龄为空请返回其他。)
select device_id, gender,
case
when age >= 25 then ‘25岁及以上’
when age >= 20 then ‘20-24岁’
when age < 20 then ‘20岁以下’
else ‘其他’
end as age_cut
from user_profile
24.想要计算出2021年8月每天用户练习题目的数量,请取出相应数据。
select day(date) as day, count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where month(date)=8 and year(date)=2021 // where date like “2021-08%”
group by date
user_submit
| device_id | profile | blog_url |
|---|---|---|
| 2138 | 180cm,75kg,27,male | http:/ur/bisdgboy777 |
| 3214 | 165cm,45kg,26,female | http:/url/dkittycc |
| 6543 | 178cm,65kg,25,male | http:/ur/tigaer |
| 4321 | 171 cm,55kg,23,female | http:/url/uhksd |
| 2131 | 168cm,45kg,22,female | http:/url/sydney |
25.对于申请参与比赛的用户,blog_url字段中url字符后的字符串为用户个人博客的用户名,现在运营想要把用户的个人博客用户字段提取出单独记录为一个新的字段,请取出所需数据
select device_id, substring_index(blog_url, ‘/‘, -1) as user_name
//负数代表从右往左 -1代表最后一个/后面 正数代表代表从左往右 1代表第一个/后面
from user_submit
26.统计每个性别的用户分别有多少参赛者,请取出相应结果
select substring_index(profile, ‘,’, -1) as gender, //最后一个字符串是性别
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
27.统计每个年龄的用户分别有多少参赛者,请取出相应结果
SELECT
substring_index(substring_index(profile, “,”, -2), “,”, 1) as age,
拿到年龄xxkg 把kg去掉赋给age
COUNT(device_id ) as number
FROM user_submit
GROUP BY age;
28.现在运营想要找到每个学校gpa最低的同学来做调研,请你取出每个学校的最低gpa。
//SELECT device_id,
university,
min(gpa) as gpa 这代码是错的 有聚合函数min() where失效了 可用having语句FROM user_profile
//GROUP BY university
正确代码:
select device_id, university,gpa
from user_profile
where (university, gpa) in (
select university,min(gpa)
from user_profile
group by university )
order by university
29.编写 SQL 语句,返回顾客 ID(cust_id)、顾客名称(cust_name)和登录名(user_login),其中登录名全部为大写字母,并由顾客联系人的前两个字符(cust_contact)和其所在城市的前三个字符(cust_city)组成。提示:需要使用函数、拼接和别名。
select
cust_id,cust_name,
upper(concat(left(cust_contact,2),left(cust_city,3))) as user_login
cust_contact 前两个字符 拼接cust_city前三个字符赋给user_login
from Customers
30.编写 SQL 语句,返回 2020 年 1 月的所有订单的订单号(order_num)和订单日期(order_date),并按订单日期升序排序
select order_num,order_date
from Orders
where order_date like '2020-01%'
order by order_date;
31.使用子查询,返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表,结果无需排序。
SELECT DISTINCT cust_id
FROM Orders
WHERE order_num IN (
SELECT order_num
FROM OrderItems
WHERE item_price >= 10
)
32.编写 SQL语句,返回顾客 ID(Orders 表中的 cust_id),并使用子查询返回total_ordered 以便返回每个顾客的订单总数,将结果按金额从大到小排序
select cust_id,(select
SUM(item_price*quantity)
FROM OrderItems
WHERE OrderItems .order_num=Orders .order_num) total_ordered
from Orders
ORDER BY total_ordered DESC
33.编写 SQL 语句,返回 Customers 表中的顾客名称(cust_name)和Orders 表中的相关订单号(order_num),并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。你可以尝试用两个不同的写法,一个使用简单的等联结语法,另外一个使用 INNER JOIN。
(1)select cust_name,order_num
from Customers C,Orders O
where C.cust_id=O.cust_id
order by cust_name
(2)select cust_name,order_num
from Customers
inner join Orders
on Customers.cust_id=Orders.cust_id
order by cust_name
34.使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 OrderItems 中)购买了 prod_id 为 “BR01” 的产品,然后从 Orders 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(cust_id)和订单日期(order_date),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序
select cust_id,order_date
from Orders
``where order_num in`
(``select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id='BR01'``)
order by order_date
- SQL 100题 编写 SQL 语句,返回订单总价不小于1000 的客户名称和总额,需要计算总和(item_price 乘以 quantity)。按总额对结果进行排序,请使用INNER JOIN 语法。
select cust_name,sum(item_price*quantity) total_price
from Customers C
inner join Orders O
on C.cust_id=O.cust_id
inner join OrderItems OI
on O.order_num=OI.order_num
group by cust_name //having语句前要用group by 有聚合函数时不能使用where
having total_price>=1000
order by total_price
将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来,以便从 OrderItems表中检索产品 id(prod_id)和 quantity。其中,一个 SELECT 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 SELECT 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序
(1)
select *from OrderItemswhere quantity in (select quantity from OrderItems where quantity = 100 )or prod_id like "BNBG%"order by prod_id;
(2)
select prod_id,quantityfrom OrderItemswhere quantity =100union all//union把select语句结合以后 取的或 即满足一个条件即可select prod_id,quantityfrom OrderItemswhere prod_id like'BNBG%'order by prod_id
各种连接:推荐使用左连接
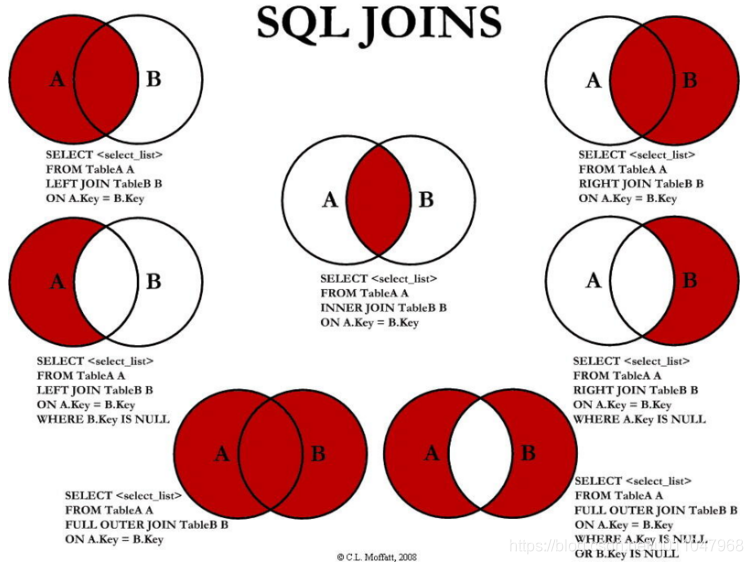
表A记录如下: 表B记录如下:
aID aNum bID bName
1 a20050111 1 2006032401
2 a20050112 2 2006032402
3 a20050113 3 2006032403
4 a20050114 4 2006032404
5 a20050115 8 2006032408
1. left join
sql语句如下:
SELECT * FROM A
LEFT JOIN B
ON A.aID = B.bID
结果如下:
aID aNum bID bName
1 a20050111 1 2006032401
2 a20050112 2 2006032402
3 a20050113 3 2006032403 左(主)表元素全会存在,即使右(副)表没有此行,
4 a20050114 4 2006032404 若没有,右表会全置为null
5 a20050115 NULL NULL
(所影响的行数为 5 行)
**大数据时删除数据(不推荐使用delete)**使用新建表,copy旧表到新表,删除旧表,重命名新表为旧表名字
1 | --创建分区表。 |
删除:
1 | DELETE FROM table_name |
插入
1 | INSERT INTO table_name |
32:牛客后台会记录每个用户的试卷作答记录到exam_record表,现在有两个用户的作答记录详情如下:
用户1001在2021年9月1日晚上10点11分12秒开始作答试卷9001,并在50分钟后提交,得了90分;
用户1002在2021年9月4日上午7点1分2秒开始作答试卷9002,并在10分钟后退出了平台。
INSERT INTO exam_record VALUES
(NULL, 1001, 9001, '2021-09-01 22:11:12', '2021-09-01 23:01:12', 90),
(NULL, 1002, 9002, '2021-09-04 07:01:02', NULL, NULL);
33:我们已经创建了一张新表exam_record_before_2021用来备份2021年之前的试题作答记录,结构和exam_record表一致,请将2021年之前的已完成了的试题作答纪录导入到该表
INSERT INTO exam_record_before_2021(uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score)
SELECT uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score
FROM exam_record
WHERE YEAR(submit_time) < '2021';
34.有一套ID为9003的高难度SQL试卷,时长为一个半小时,请你将 2021-01-01 00:00:00 作为发布时间插入到试题信息表examination_info(其表结构如下图),不管该ID试卷是否存在,都要插入成功,请尝试插入它
replace INTO examination_info //会先检查是否存在此数据,如果有则不插入,没有则插入
VALUES(NULL,9003,'SQL','hard',90,'2021-01-01 00:00:00');
或
insert INTO examination_info //不会检查是否存在此数据,直接插入
VALUES(NULL,9003,'SQL','hard',90,'2021-01-01 00:00:00');
更新
1 | UPDATE table_name |
35.把examination_info表中tag为PYTHON的tag字段全部修改为Python。
update examination_info set tag='Python' where tag='PYTHON'
36.编写SQL 语句,查找所有订购了数量至少100 个的 BR01、BR02 或BR03 的订单。你需要返回 OrderItems 表的订单号(order_num)、产品 ID(prod_id)和数量(quantity),并按产品 ID 和数量进行过滤
select order_num,prod_id,quantity
from OrderItems
where (prod_id='BR01'or prod_id='BR02'or prod_id='BR03') and quantity>=100
1 | SELECT order_num,prod_id,quantity |
37.编写 SQL 语句,返回每个订单号(order_num)各有多少行数(order_lines),并按 order_lines对结果进行升序排序。
1 | select order_num,count(*) order_lines`` |
知识点:
1、count(*),count(列名)都可以,区别在于,count(列名)是统计非NULL的行数
2、order by最后执行,所以可以使用列别名
3、分组聚合一定不要忘记加上 group by ,不然只会有一行结果
38.请从试卷作答记录表中找到SQL试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分。
select score min_score_over_avg
from exam_record,examination_info
where examination_info.tag='SQL'
and exam_record.exam_id = examination_info.exam_id
and score>=(select avg(score)`
from exam_record , examination_info
where examination_info.tag = 'SQL'
and exam_record.exam_id = examination_info.exam_id``)
order by score limit 1
union:连接两表,会去重,效率较低
union all:连接两表,不去重,效率较高
1 | SELECT EMP_ID, NAME, DEPT FROM COMPANY INNER JOIN DEPARTMENT |
触发器:触发器是与表有关的数据库对象,在满足定义条件时触发,并执行触发器中定义的语句集合。也就是由事件来触发某个操作,事件包括INSERT语句,UPDATE语句和DELETE语句;可以协助应用在数据库端确保数据的完整性。
1、创建触发器:
1.创建只有一个执行语句的触发器
例1:创建了一个名为trig1的触发器,一旦在work表中有插入动作,就会自动往time表里插入当前时间
CREATE TRIGGER 触发器名 BEFORE|AFTER 触发事件 ON 表名 FOR EACH ROW 执行语句;
2
3
-> ON work FOR EACH ROW
-> INSERT INTO time VALUES(NOW());
2.创建有多个执行语句的触发器
CREATE TRIGGER 触发器名 BEFORE|AFTER 触发事件
ON 表名 FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
执行语句列表
END;
例2:定义一个触发器,一旦有满足条件的删除操作,就会执行BEGIN和END中的语句
2
3
4
5
trigger_event: { INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE }//触发器可以执行的三种操作
trigger_order: { FOLLOWS | PRECEDES } other_trigger_name
1 | mysql> CREATE TRIGGER trig2 BEFORE DELETE |
2、NEW与OLD详解
MySQL 中定义了 NEW 和 OLD,用来表示触发器的所在表中,触发了触发器的那一行数据,来引用触发器中发生变化的记录内容,具体地:
①在INSERT型触发器中,NEW用来表示将要(BEFORE)或已经(AFTER)插入的新数据;
②在UPDATE型触发器中,OLD用来表示将要或已经被修改的原数据,NEW用来表示将要或已经修改为的新数据;
③在DELETE型触发器中,OLD用来表示将要或已经被删除的原数据;
使用方法:
NEW.columnName (columnName为相应数据表某一列名)
另外,OLD是只读的,而NEW则可以在触发器中使用 SET 赋值,这样不会再次触发触发器,造成循环调用
1 | mysql> CREATE TRIGGER upd_check BEFORE UPDATE ON account |
3、查看触发器
(1)SHOW TRIGGERS语句查看触发器信息
mysql> SHOW TRIGGERS\G;
……
结果,显示所有触发器的基本信息;无法查询指定的触发器。
(2)、在information_schema.triggers表中查看触发器信息
mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.triggers\G
4、删除触发器
DROP TRIGGER [IF EXISTS] [schema_name.]trigger_name
创建数据库:CREATE DATABASE dbname;
删除数据库:DROP DATABASE [ IF EXISTS ] name
创建表格:
1 | CREATE TABLE table_name( |
删除表格:DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table_name;
增删改查:INSERT DELETE/TRUNCAT UPDATE SELECT
(1**)增加表中数据**:INSERT INTO…VALUES…
1 | INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME (column1, column2, column3,...columnN) |
- 嵌套增加
1 | INSERT INTO table_name [ (column1 [, column2 ]) ] |
(2)删除表中数据:
1 | DELETE FROM table_name WHERE [condition]; |
或
1 | TRUNCATE TABLE table_name; |
- 嵌套
1 | DELETE FROM TABLE_NAME |
(3)更新/修改表中数据:UPDATE 表名 SET … WHERE…
1 | UPDATE table_name |
- 嵌套
1 | UPDATE table |
ALTER TABLE 语句用于在已有的表中添加、删除或修改列。
alter add;添加列 alter change;改列名 alter modify;修改列数据类型
如需在表中添加列,请使用下面的语法:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype
如需删除表中的列,请使用下面的语法(请注意,某些数据库系统不允许这种在数据库表中删除列的方式):
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name
要改变表中列的数据类型,请使用下面的语法:
ALTER TABLE table_name
MODIFY COLUMN column_name datatype
(4)查找表中数据:SELECT…FROM…
1 | SELECT column1, column2,...columnN FROM table_name; |
- 嵌套子查询
1 | SELECT column_name [, column_name ] |
例:
1.带in的子查询
select sno, snamefrom studentwhere sno in (select sno from sc where cno='C001');
2.带比较运算符的子查询
select cno from sc as xwhere score >(
select avg(score) from sc as y where x.sno=y.sno and x.sno = '2016110129')and sno = '2016110129';
3.带any(some)或all的子查询
select cno from scgroup by cnohaving COUNT(*) >= all(select COUNT(*) from sc group by cno);
4.带exists的子查询
#列出选修了C001课程的学生的学号、姓名select sno,sname from studentwhere exists(select * from sc where sc.sno=student.sno and cno='C001');
5.基于派生表的查询
select sc.sno,total_cre,avg(score) from
(select sc``, sno,SUM(ceredit) as total_cre from sc,course``` where sc.cno=course.cno
and score >= 60
group by sno
having SUM(ceredit) >= 8) as temptable //一定要取别名!
where temptable.sno=sc.sno group by sc.sno,sum_cre;`
//有select 后面接子查询;也有from后面接子查询(相当于试图),最后要其别名
- where型子查询:把内层查询的结果作为外层查询的比较条件
(1)SELECT goods_id,goods_name,shop_price
FROM goods
WHERE goods_id = (SELECT MAX(goods_id) FROM goods)
(2)SELECT goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price
FROM goods
WHERE goods_id IN (SELECT MAX(goods_id) FROM goods GROUP BY cat_id);
from型子查询:把内层的查询结果当成临时表,供外层sql再次查询。查询结果集可以当成表看待。临时表要使用一个别名
(1) SELECT goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price
FROM (SELECT goods_id,goods_name,cat_id,shop_price
FROM goods
ORDER BY cat_id ASC,goods_id DESC) AS tmp
GROUP BY cat_id;
连接:union /union all
**union:**连接两表,去重,效率低
**union all:**连接两表,不去重,效率高
//使用union以后 上下语句只能使用一个order by
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
- ORDER BY cust_name; × //不能在此使用order by
UNION
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'IL'
ORDER BY cust_name;
group by用法:
- 当select使用了聚合函数时,只会产生一个数据,若要产生多个数据,则后面需加个group by
GROUP BY 叙述句搭配聚合函数 (aggregation function) 使用,是用来将查询结果中特定栏位值相同的资料分为若干个群组,而每一个群组都会传回一个资料列。若没有使用 GROUP BY,聚合函数针对一个 SELECT 查询,只会返回一个汇总值。
select prod_name,count(OrderItems.prod_id) orders
from Products p
left join OrderItems
on p.prod_id=OrderItems.prod_id
group by prod_name //无这个则输出只有一个
order by prod_name
2.去重,代替distinct去重
各种函数:
timestampdiff(minute, begin, end) 算时间
例/timestampdiff(minute,start_time,submit_time)<5
2.if(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false) 条件函数
例if(score is null,0,score)
3.round(x,d) ,x指要处理的数,d是指保留几位小数
例round(**sum(if(score is null,0,score))/count(uid) **, 0 )
round(x) ,其实就是round(x,0),也就是默认d为0
4.char_length(s) 返回字符串 s 的字符长度
5.concat(s1,s2…sn) 字符串 s1,s2 ..sn等多个字符串合并为一个字符串
例 CONCAT(substring(nick_name,1,10),”…”) nick_name前10个字符和 ‘…’拼接
6.left(s,n) 返回字符串 s 的前 n 个字符
7.RIGHT(s,n) 返回字符串 s 的后 n 个字符
8.replace(s,s1,s2) 将字符串 s2 替代字符串 s 中的字符串 s1
9.reverse(s) 将字符串s的顺序反过来
10.substr(s, start, length) 从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串11.substring(s, start, length) 从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串,等同于 SUBSTR(s, start, length)
12.date_format(d,f) 按表达式 f的要求显示日期 d
例 date_format(start_time, ‘%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s’)
day(d)/month(d)/year(d) 返回日期值 d 的日期部分/月份/年份 //DAY(“2017-06-15”)
count(): count(1) 1代表这个表达式不为 NULL 的记录 count(*) count(字段)
sum(if( )) 、count(if( ))
sum(if(fenlei=’分类1’,1,0)) A
即:如果是’分类1’的则返回1,否则返回0,对返回辅助列进行求和,得到符合此条件的数据的总和
满足条件的对象求和,即统计
1的数量count(if(fenlei=’分类2’,1,0)) B
即:如果是’分类2’的则返回1,否则返回0,但是因为都有数值,count对所有有值的列进行计数
无视条件求和,即统计
0或者1的数量
case..when语句:CASE
WHEN SCORE = ‘A’ THEN ‘优’
WHEN SCORE = ‘B’ THEN ‘良’
WHEN SCORE = ‘C’ THEN ‘中’
ELSE ‘不及格’
END
例:SELECT STUDENT_NAME,
(CASE
WHEN score < 60 THEN ‘不及格’
WHEN score >= 60 AND score < 80 THEN ‘及格’
WHEN score >= 80 THEN ‘優秀’
ELSE ‘異常’
END) AS REMARK FROM TABLE
with语句:给子查询语句取别名,下次就能直接取。
with u1 as
(select id, sum(amount) as num from pay where pay_time >= 1493568000 and pay_time < 1494172800 group by id),
u2 as(select id, sum(amount) as total from pay where pay_time < 1494172800 group by id)
select u1.id, pinfo.sid, u1.num, u2.total from u1, u2, pinfo where u2.id = u1.id and pinfo.id = u1.id;
窗口函数:窗口函数原则上只能写在select子句中
1 | <窗口函数> over (partition by <用于分组的列名> |
(1)专用窗口函数:rank, dense_rank, row_number
例:select row_number() over(partition by Uid order by score) as A
//在原表的基础上再加一列,普通聚合函数只是查询出某列
(2)聚合函数:sum. avg, count, max, min
例:select sum(salary) over( partition by Uid order by score ) as B
salary/sum(salary) over( ) as B
